![[de]](../../Logos/flag_ger.gif)
![[it]](../../Logos/flag_it.gif)
Particulars:
General:
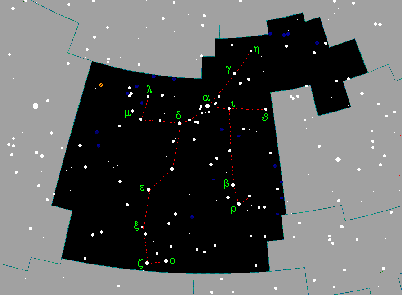
One of the larger constellations of the northern hemisphere. The northern
border reaches as high as DECL=+59 degrees, the southern border
reaches DECL=+31 degrees (touching Aries
and Taurus). From east to
west this constellation extends from roughly RA=4h 50m to RA=1h 30m.
Perseus gives name to one of the
constellation families.
The figure of Perseus ist thought to held the head of Medusa in his
hand (the star beta Per represents the evil eye of her).
Stars and other objects
The leading star alpha Per, called Marfak or
Algenib, is an F5 supergiant with 1.79 mag, which makes it,
together with alpha UMa, the 32nd
brightest star
in the sky. It lies
within a widely scattered cluster of stars making it an interesting region
for binoculars.
Small telescopes may have a problem in resolving the 8th mag companion (an
A2 main sequence star) of the B0.5 main sequence star epsilon Per.
The brighter component is of 2.89 mag and therefore the fainter component
may just be lost in the intense glow of the first one.
Another pair with a large brightness contrast is zeta Per, a B1
supergiant of 2.85 mag and its 9th mag companion.
An attractive pair for small telescopes is eta Per: a red and a blue
star of 4th and 9th mag sitting in a star rich field.
The eclipsing binary beta Per, called Algol is one
of the most famous variable stars in the sky. The two stars revolve each
other every 2 days and 21 hours. During the eclipsing phase the brightness
varies from 2.2 mag to 3.5 mag.
The brightness of the variable star rho Per varies semiregularily
from 3rd mag to 4th mag. This changings are happening nearly monthly.
An easy object for small telescopes is
M34. This cluster is bright and
quite large. In a dark night it can be seen with the naked eye. Individual
stars can be resolved even with small optical power.
The two open star cluster NGC 869 and NGC 884, commonly named
h Per and chi Per, are the famous
Double Cluster
of Perseus (located at the northern edge). These two related star
clusters belong to the best targets for small instruments. Viewed in a clear
dark night the clusters appear to the naked eye as one hazy patch in the sky.
Using little optical help stars scattered over 0.5 degrees of the sky are
revealed. With small scopes some of the red stars can be seen in NGC 884.
It is less bright and less rich cluster of the pair. The distance to that
pair is estimated to be about 7000 lightyears.
To observe NGC 1528 most effectively one should use low telescopic
power.
The planetary nebula M 76, called
Little Dumbbell Nebula, is a quite faint object, but with
some nice irregular extensions in its appearence. For more information please
refer to the Messier database.
The Perseids are one of the
most famous and most glorious meteor showers. It duration extends from
July 23th to August 22nd. The maximum occurs on August 12th/13th, but
it is also worth to observe this shower before and after this date. The
Perseids meteors are known to be bright; sometimes the explode and leave
trains.
The existence of the meteor shower
Zeta Perseids has been
discovered 1947. It is one of the daylight showers. The meteors fall
between May 20th and July 5th; the maximum occurs on June 13th. See Gary
Kronk's database about meteors showers for detailed information.
Mythological Background:
![[Constellations]](../../Logos/constS_s.gif)
![[Home]](../../Logos/maa_s.gif)